Introduction
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects devices within a small area, such as a home, school, office, or building.
LANs allow devices to share data, printers, internet, and services securely and efficiently.
This blog explains LAN concepts step by step in very simple language, inspired by TryHackMe – Network Fundamentals.
What is LAN?
LAN stands for Local Area Network.
Examples of LAN:
Home Wi-Fi network
Office computer network
School computer lab
All devices in a LAN can communicate with each other directly.
LAN Topologies (Network Designs)
In networking, topology means the shape or design of a network.
1️⃣ Star Topology
How it works:
All devices connect to a central device like a switch.
Advantages:
Easy to add new devices
Fast and reliable
Easy to manage
Disadvantages:
Expensive (more cables + switch)
If the switch fails, the whole network stops
Used in:
Homes, offices, schools (most common topology)
2️⃣ Bus Topology
How it works:
All devices share one main cable (backbone).
Advantages:
Cheap to install
Less cabling
Disadvantages:
Network becomes slow if many devices are active
If the backbone cable breaks, the whole network fails
Hard to troubleshoot
Used in:
Old networks (rare today)
3️⃣ Ring Topology
How it works:
Devices form a circular loop, and data travels in one direction.
Advantages:
No data collision
Easy fault detection
Disadvantages:
If one device or cable fails, the whole network stops
Data may travel slowly
Used in:
Very rare today
What is a Switch?
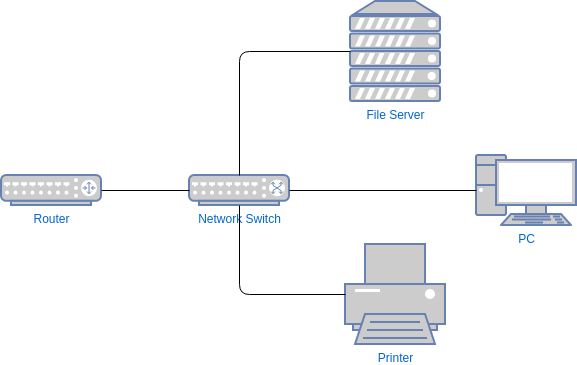
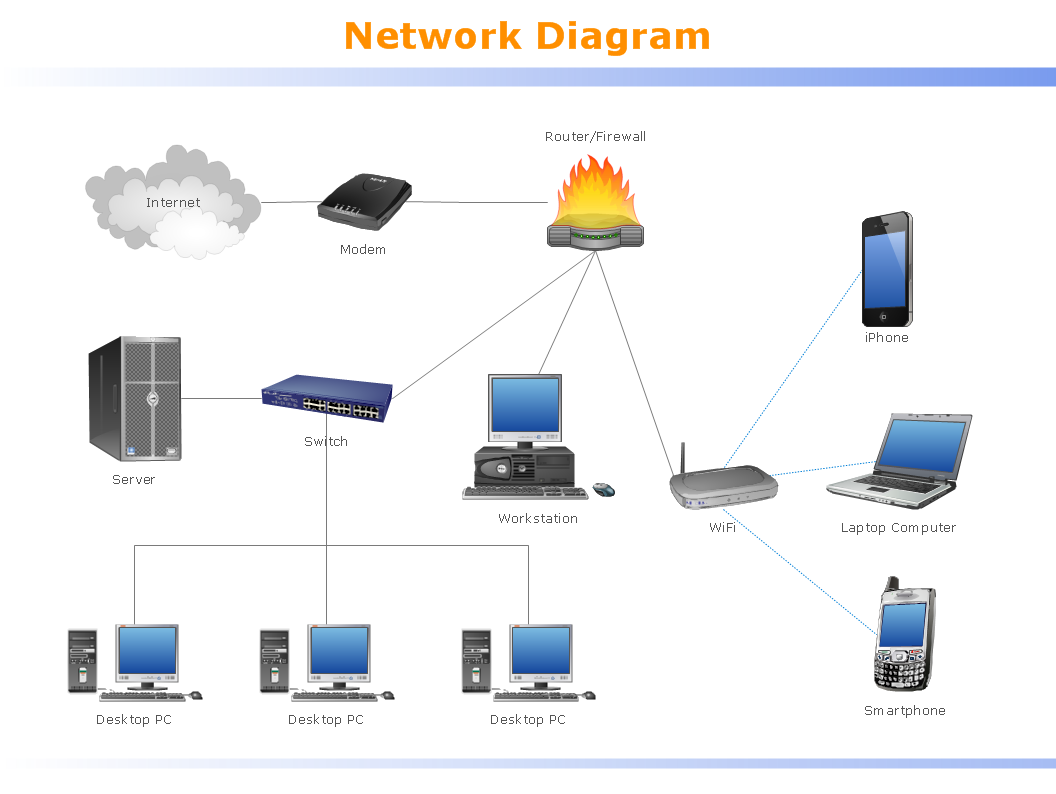
A switch connects multiple devices in a LAN and sends data only to the correct device.
Why switch is better than hub:
Hub sends data to all devices
Switch sends data only to the target device
Benefits:
Faster network
Less traffic
More secure
What is a Router?
A router connects different networks and sends data between them.
Example:
Home LAN ↔ Internet
Office LAN ↔ Branch office
The job of a router is called Routing.
What is Subnetting?
Subnetting means dividing one large network into smaller networks.
Simple example
Office has departments:
HR
Finance
Accounts
Subnetting helps:
Separate departments
Improve security
Reduce network traffic
Subnet Mask Explained
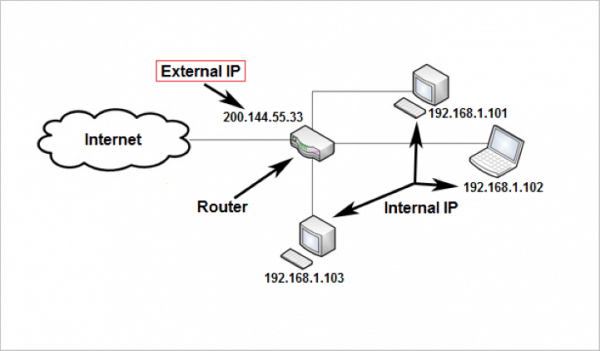
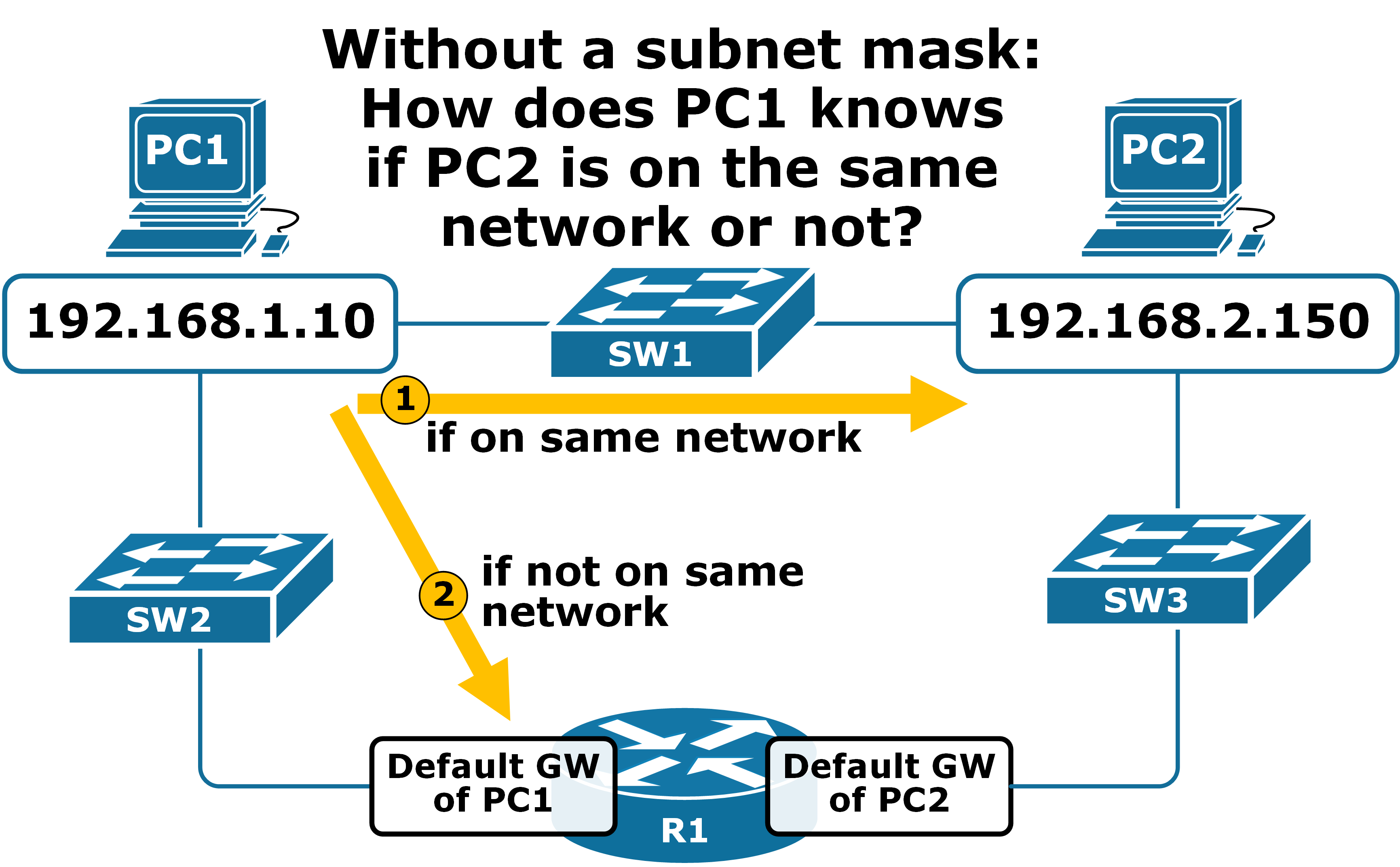
Subnet mask has 32 bits
Written like an IP address
Range of each octet: 0–255
Example:
IP Address : 192.168.1.100
Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.0
Types of Addresses in a Subnet
1️⃣ Network Address
Identifies the network itself
Example:
192.168.1.0
2️⃣ Host Address
Identifies devices in the network
Example:
192.168.1.100
3️⃣ Default Gateway
Sends data to other networks
Usually:
192.168.1.1 or 192.168.1.254
What is ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)?
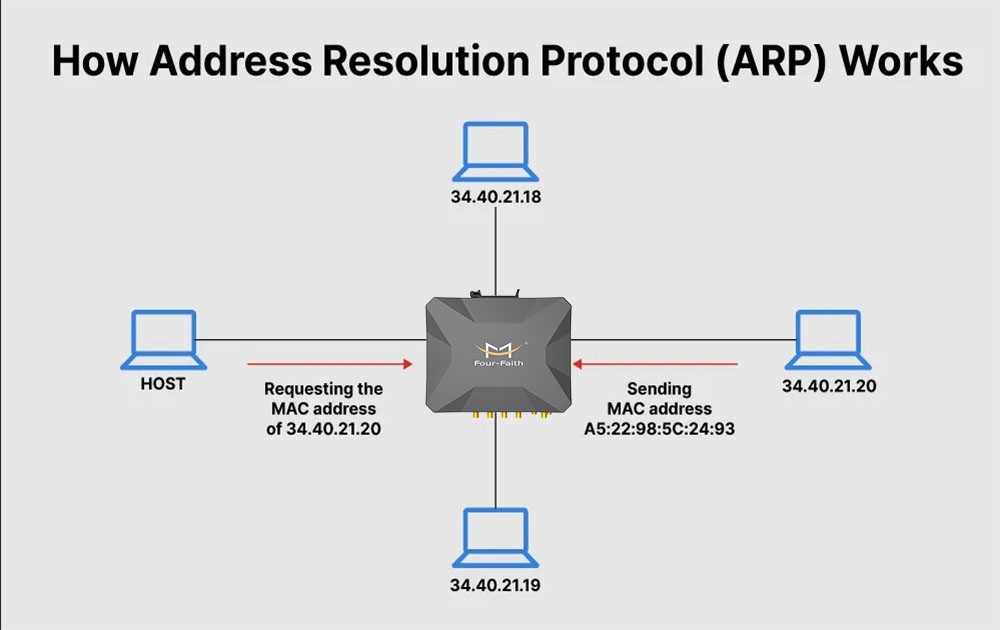
Devices use two identities:
IP Address
MAC Address
ARP connects these two.
How ARP works:
Device sends ARP Request
“Who has this IP?”Target device replies with MAC Address
Mapping is stored in ARP Cache
ARP helps devices communicate inside a LAN.
What is DHCP?

DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to devices.
DHCP Process (DORA):
Discover – Device asks for IP
Offer – Server offers IP
Request – Device accepts
ACK – Server confirms
Without DHCP, IPs must be set manually, which is slow and error-prone.
Why These Concepts Are Important?
Understanding LAN fundamentals helps in:
Networking jobs
Cybersecurity
Ethical hacking
Firewall & server configuration
Troubleshooting network issues
Conclusion
LAN is the foundation of networking.
Quick recap:
LAN connects devices locally
Topologies define network design
Switch connects devices efficiently
Router connects networks
Subnetting improves security
ARP links IP to MAC
DHCP automates IP assignment
If you understand these basics, advanced networking becomes easy.



No comments:
Post a Comment