Tech Guardians – Cyber Range Based Course
Network Security Phase–2: Active Reconnaissance
Passive reconnaissance builds awareness without touching the target. The next stage — active reconnaissance — involves direct interaction with systems to identify network paths, open services, technologies, and system behavior.
Inside the Tech Guardians Cyber Range, students practice these techniques in a controlled environment where learning happens safely, legally, and practically.
🔎 What is Active Reconnaissance?
Active reconnaissance requires making a connection to the target system. This interaction may be:
Visiting a website
Checking open ports
Sending network packets
Connecting to services such as SSH, HTTP, or SMTP
Because direct contact is made, logs can record:
Client IP
Connection time
Duration
Requested resources
Therefore, active reconnaissance must only be performed with proper authorization.
🌐 Web Browser as a Reconnaissance Tool

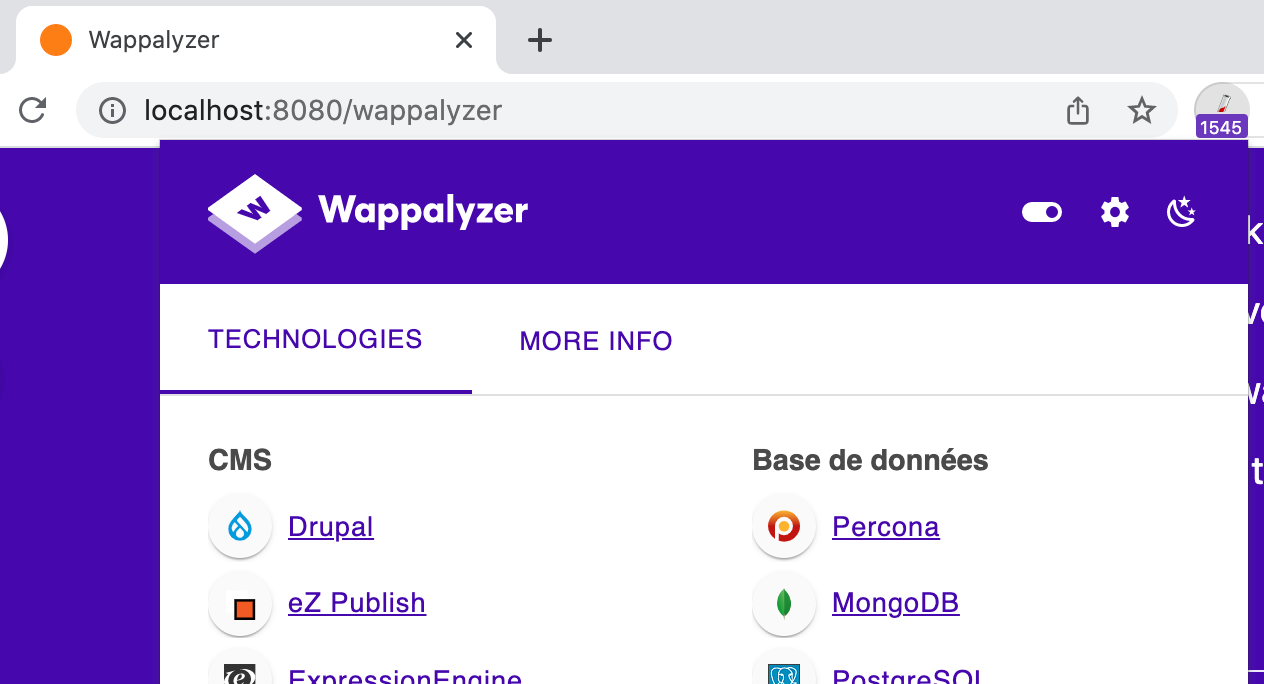
A web browser is one of the most powerful reconnaissance tools available on every system.
Key Capabilities
Inspect page source and JavaScript
View cookies and session data
Discover site structure
Identify backend technologies
Useful Extensions
FoxyProxy → quick proxy switching (Burp Suite workflows)
User-Agent Switcher → simulate different devices and browsers
Wappalyzer → detect frameworks, servers, CMS, analytics
Default Transport Ports
HTTP → TCP 80
HTTPS → TCP 443
Custom ports can be accessed using:
https://IP:PORT
📡 Ping — Checking System Availability
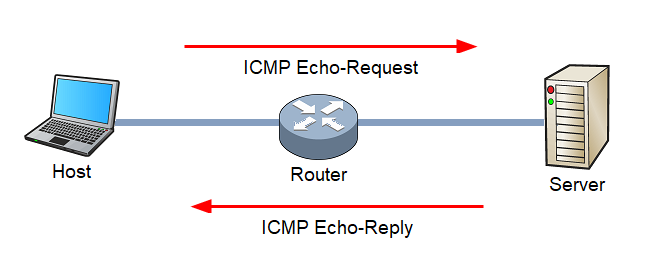

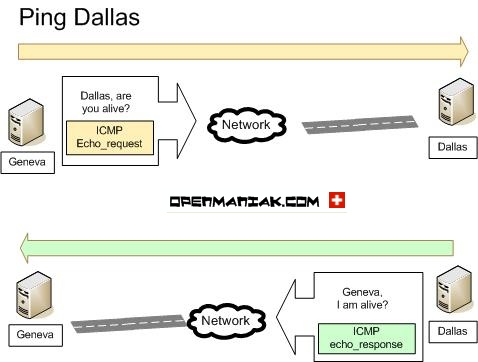
Ping verifies whether a system is online by sending an ICMP Echo Request and waiting for an Echo Reply.
Uses
Confirm host availability
Measure latency
Check network path reliability
Example
Linux:
ping -c 5 MACHINE_IP
Important Concepts
Uses ICMP protocol
ICMP header size → 8 bytes
Windows Firewall blocks ping by default
Possible reasons for no response:
System offline
Network issue
Firewall blocking ICMP
🛰 Traceroute — Mapping Network Path
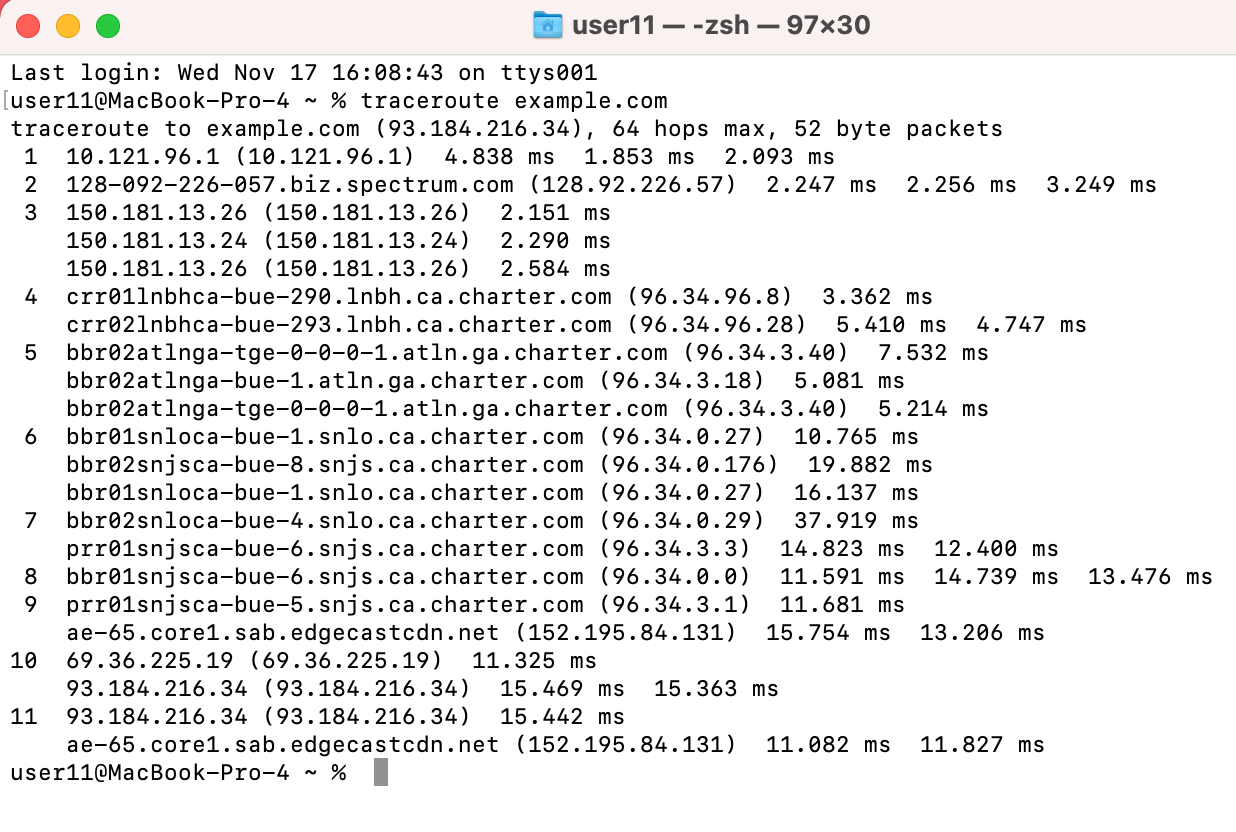
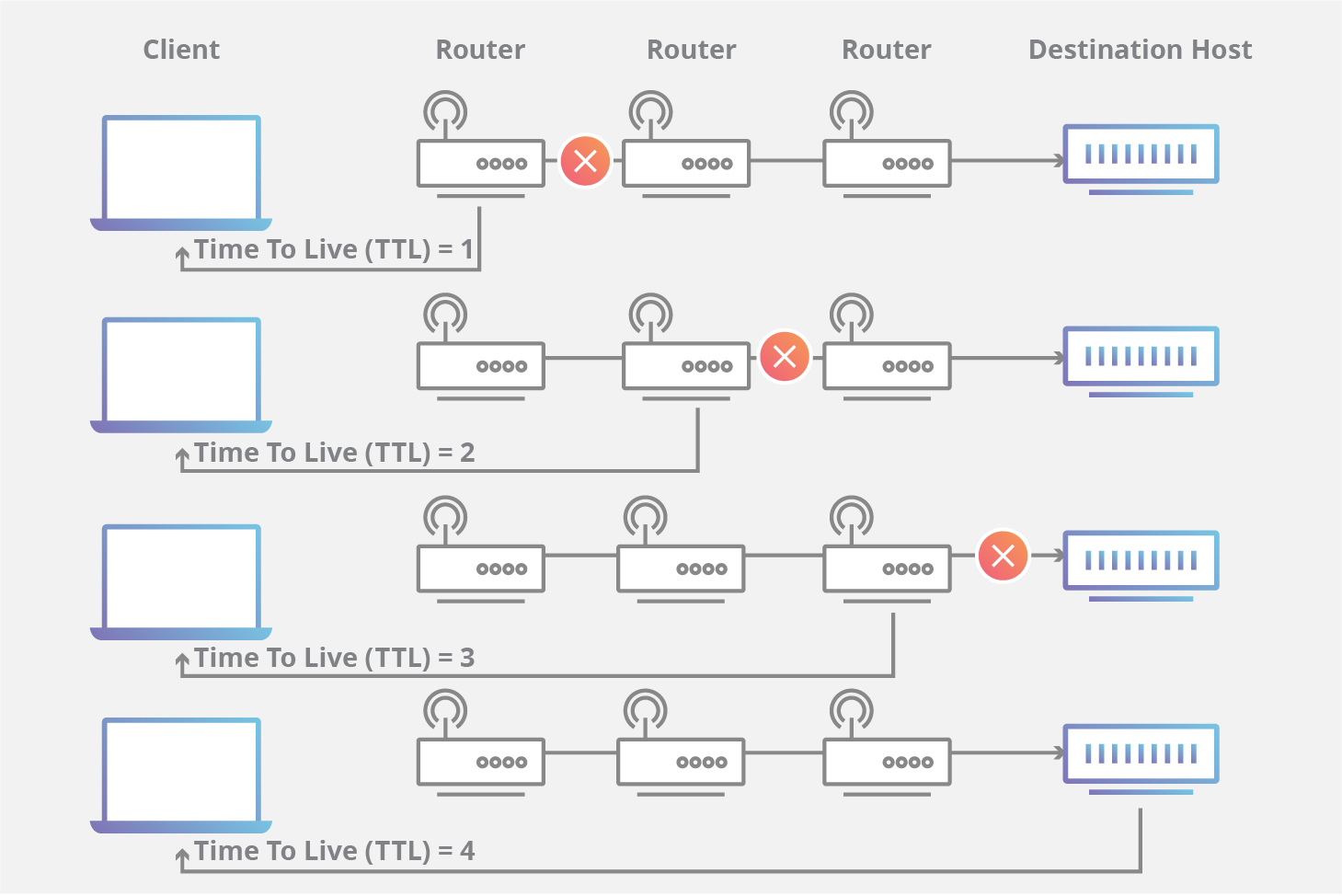
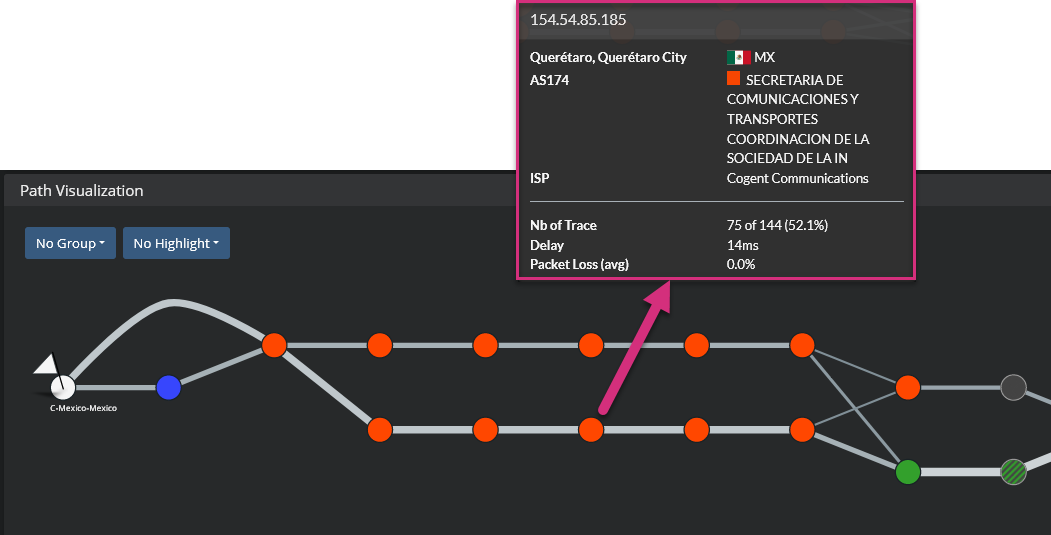
Traceroute reveals the routers (hops) between your system and the target.
It works by manipulating TTL (Time To Live) values to force routers to respond with ICMP messages.
What It Shows
Number of routers
Network latency per hop
Route changes over time
Commands
Linux/macOS:
traceroute MACHINE_IP
Windows:
tracert MACHINE_IP
Key Insight: Internet routes are dynamic, so results may vary.
💻 Telnet — Banner Grabbing and Service Testing

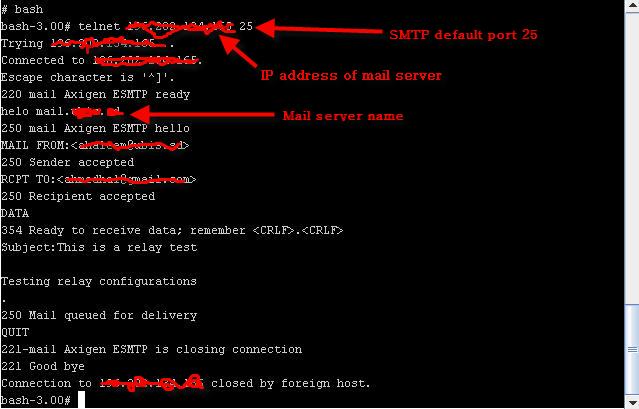
Telnet is an old remote administration protocol (port 23) that transmits data in plaintext. Although insecure for login, it is valuable for reconnaissance.
Uses
Connect to any TCP port
Grab service banners
Identify server type and version
Example:
telnet MACHINE_IP 80
GET / HTTP/1.1
host: test
This may reveal:
Server: Apache / Nginx
⚡ Netcat (nc) — The Swiss Army Knife

Netcat supports TCP and UDP and can act as both client and server.
Capabilities
Banner grabbing
Port connectivity testing
File transfer
Reverse shells
Simple chat channels
Example — Client
nc MACHINE_IP 80
Example — Server
nc -lvnp 1234
Common Options:
| Option | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -l | Listen mode |
| -p | Specify port |
| -n | No DNS lookup |
| -v | Verbose |
| -k | Keep listening |
🧠 Combining Tools for Recon Workflow
Basic scanning workflow:
Ping → Check if host is alive
Traceroute → Map network path
Telnet / Netcat → Identify open ports and services
Browser DevTools → Detect web technologies
Professional scanners like Nmap automate this process — covered in later course modules.
🎯 Learning Outcome in Tech Guardians Cyber Range
Students learn:
Real-world recon methodology
Safe testing inside isolated labs
Tool chaining and automation basics
How attackers gather intelligence
How defenders detect recon activity